3.15. Equivalent Loops#
When programming, you’ll find that there are often multiple ways to write your program and have it do the same thing! Have a look at the examples below. You will find that in each example, the programs do the exact same thing.
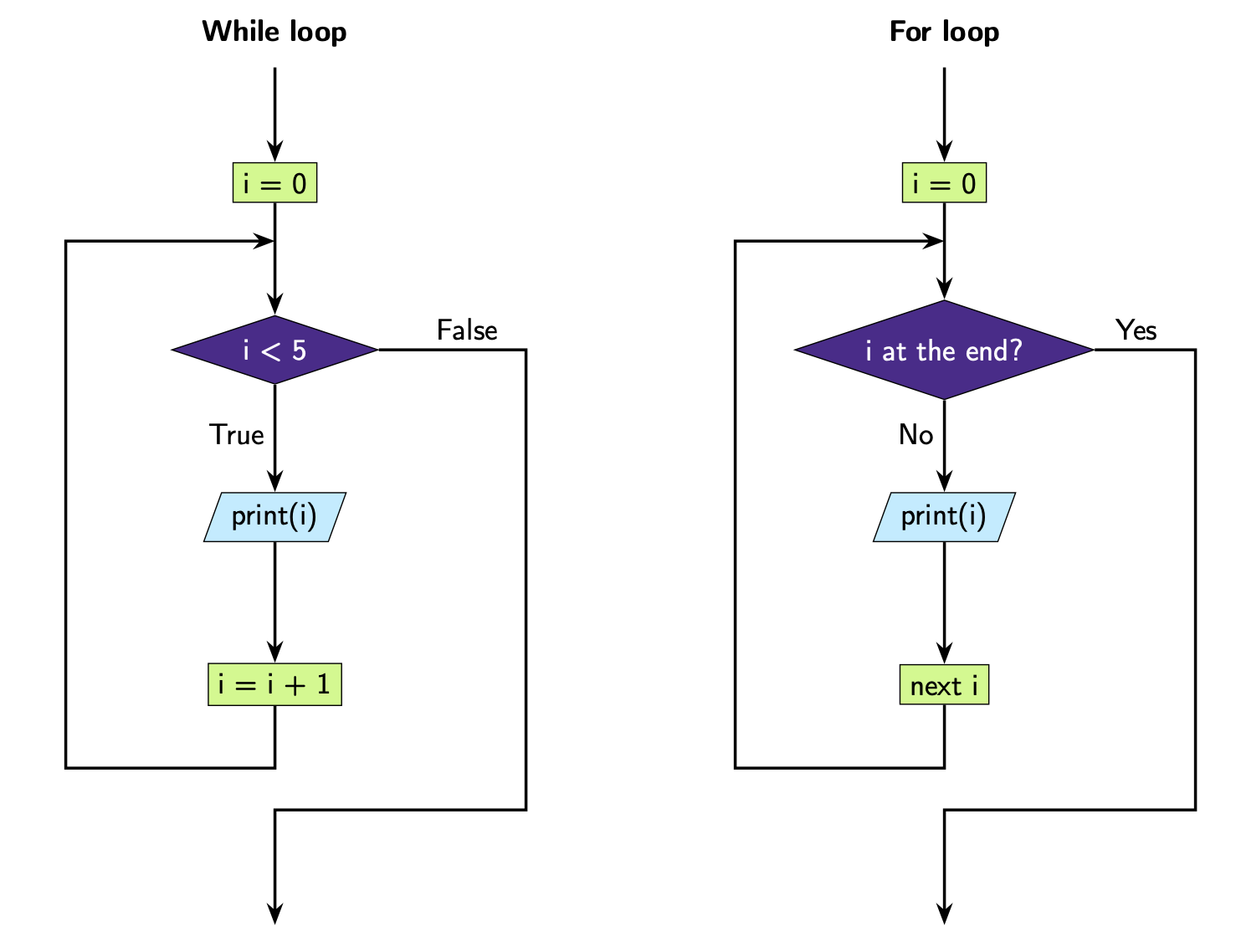
Example 1: Count 0 to 4
i = 0
while i < 5:
print(i)
i = i + 1
0
1
2
3
4
for i in range(5):
print(i)
0
1
2
3
4
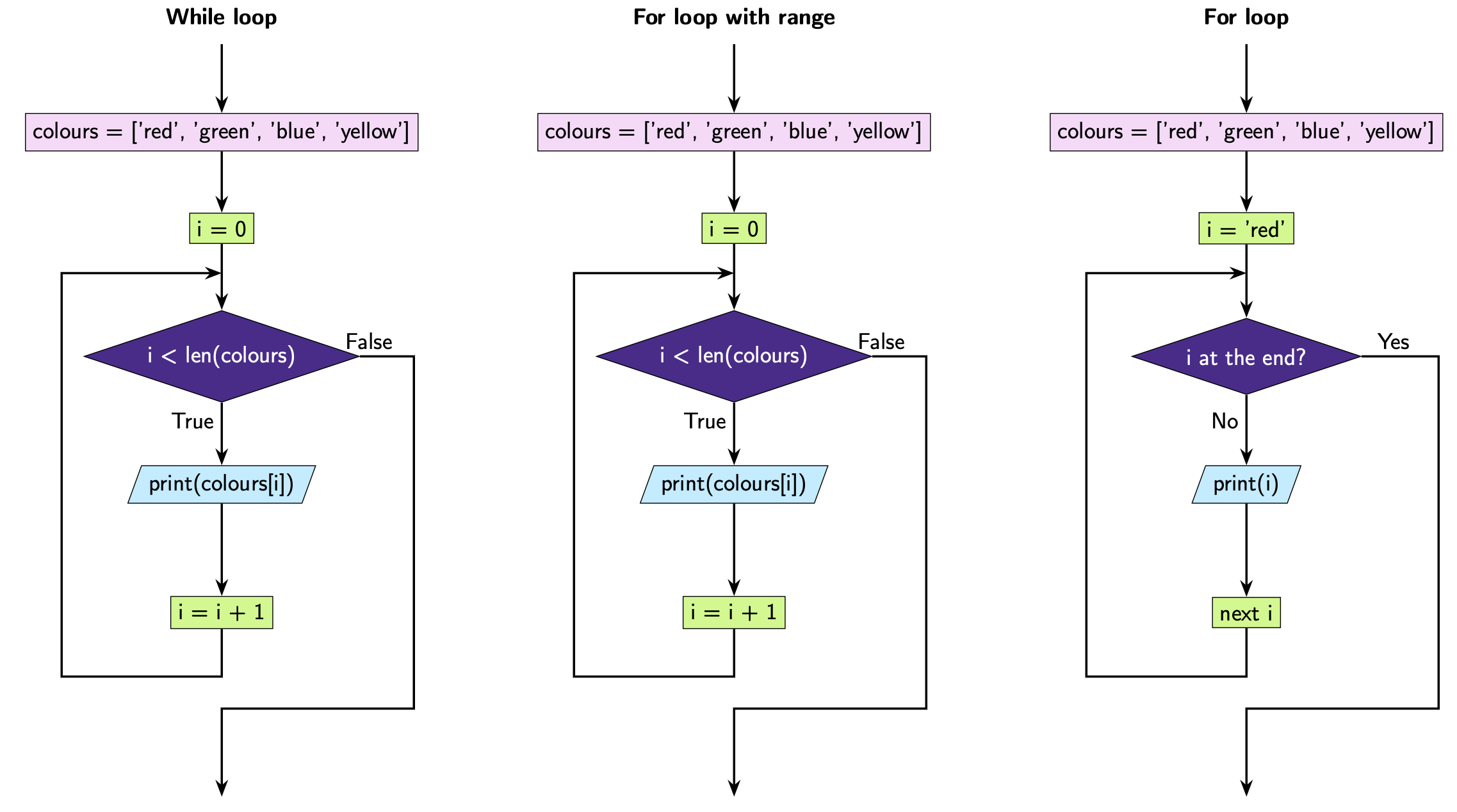
Example 2: Print each colour
colours = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow']
i = 0
while i < len(colours):
print(colours[i])
i = i + 1
red
green
blue
yellow
colours = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow']
for i in range(len(colours)):
print(colours[i])
red
green
blue
yellow
colours = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow']
for i in colours:
print(i)
red
green
blue
yellow
When you write a loop you will have to choose whether you use a for loop or
a while loop. Often, it won’t matter which one you choose as both will
work. But in general, you would use:
a
whileloop if you don’t know how many times to repeat your code - instead, you will terminate your loop once a certain condition is meta
forloop if you know how many times you want to repeat your code
Question 1
Which of the following while loops produces the same output as the for loop shown below?
for i in range(5, 10):
print(i)
i = 0 while i < 10: print(i) i = i + 1
i = 5 while i < 10: print(i) i = i + 1
i = 0 while i < 10: print(i) i = i + 5
i = 1 while i < 10: print(i) i = i + 5
Question 2
Will the following two programs produce the same output?
Program 1
words = ['rain', 'one', 'light', 'owl', 'ranch']
for i in range(len(words)):
print('b{}'.format(words[i]))
Program 2
words = ['rain', 'one', 'light', 'owl', 'ranch']
for i in words:
print('b' + i)
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 3
Construct a for loop that is equivalent to the following while loop.
fries = ['curly', 'shoestring', 'waffle', 'crinkle', 'wedge']
i = -1
while i > -len(fries):
print(fries[i])
i = i - 1
Solution
Solution is locked
