3.7. While Loops#
While loops can be used to repeat code.
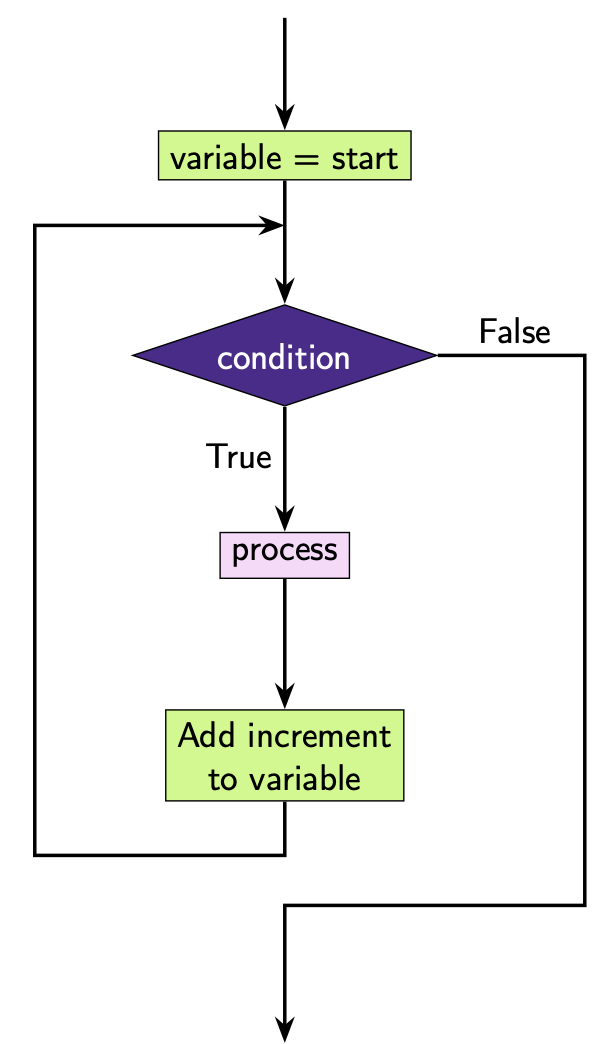
The structure of a while loop is:
while condition:
# code that executes while condition is true
Here is an example:
i = 0
while i < 3:
print(i)
i = i + 1 # increment i by 1
0
1
2
Note
Another way you can increment i by 1 is using i += 1. This is
equivalent to i = i + 1. Similarly you can decrease i by 1 using
i -= 1, which is equivalent to i = i - 1. Actually the += and
-= notation will work for any number i += 3 increase i by 3 and
i -= 5 decrease i by 5.
What’s happening here?
We can see that the condition we have set for our while loop is i < 3.
At the first iteration i = 0. This means the condition is True. We
execute the code block:
print(i)
i = i + 1
This means that we output:
0
At the second iteration i = 1. This means the condition is True.
Again, we execute the code block and we output:
1
At the third iteration i = 2. This means that the condition is
True. Again, we execute the code block and we output:
2
At the fourth iteration i = 3. This means that the condition is
False. We do not execute the code block.
This is how we can represent this code diagrammatically.
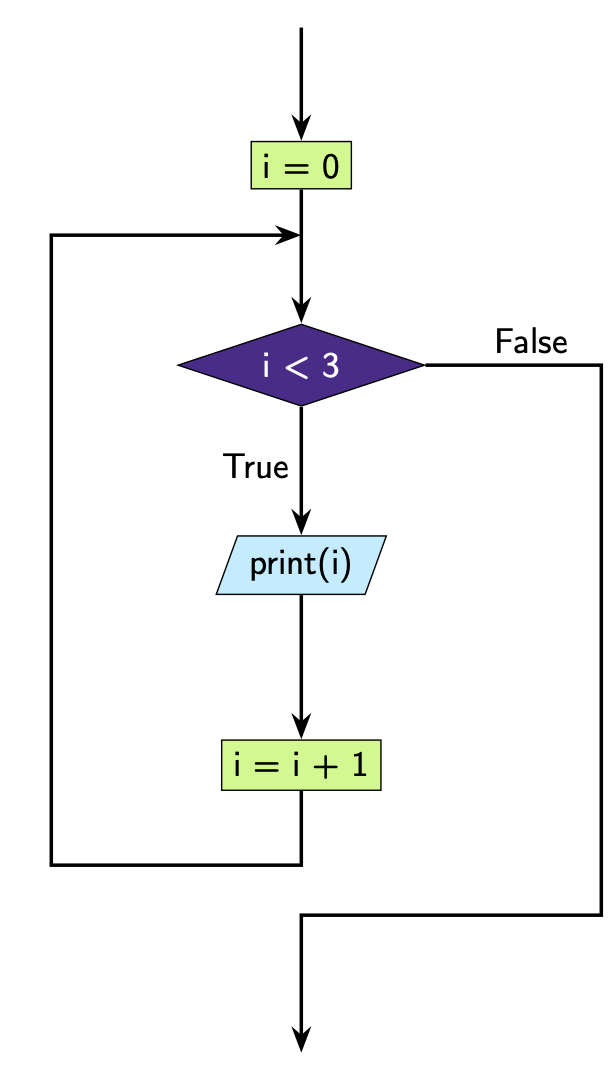
Here i = 0 and i = i + 1 are processes that are happening within
the program but aren’t being shown to the user. This means we represent these
with rectangles in the flowchart. The print statement results in
output to the user so we represent it with a parallelogram. Here we
colour the processes related to i in green to identify it as the
variable related to the loop, but the colouring is non-standard and most of the
time these diagrams will be shown in black and white.
Note that we don’t always have to increment by 1 and we don’t always have to
start at i = 0. For example, we might want to print out all the odd numbers
less than 10. We can do so with the following.
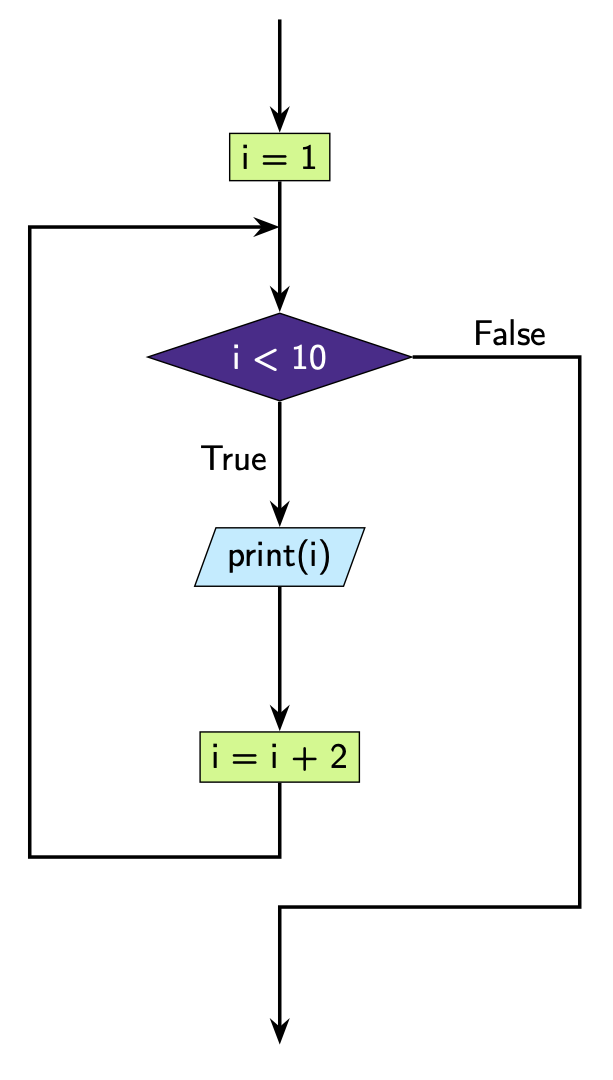
i = 1
while i < 10:
print(i)
i = i + 2 # increment i by 2
1
3
5
7
9
What’s happening here?
We can see that the condition we have set for our while loop is i < 10.
At the first iteration i = 1. This means the condition is True. We
execute the code block:
print(i)
i = i + 2
This means that we output:
1
At the second iteration i = 3. This means the condition is True.
Again, we execute the code block and we output:
3
At the third iteration i = 5. This means that the condition is
True. Again, we execute the code block and we output:
5
At the fourth iteration i = 7. This means that the condition is
True. Again, we execute the code block and we output:
7
At the fifth iteration i = 9. This means that the condition is
True. Again, we execute the code block and we output:
9
At the sixth iteration i = 11. This means that the condition is
False. We do not execute the code block.
This is how we can represent this code diagrammatically.
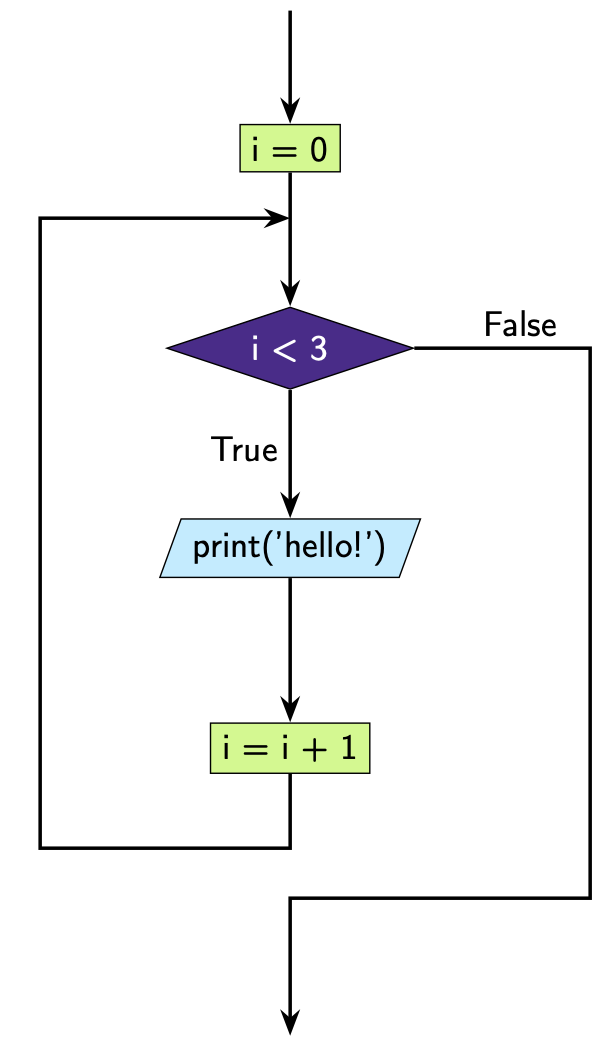
Question 1
What do you think the output of the following will be?
i = 0
while i < 3:
print('hello!')
i = i + 1
1 2 3
hello! hello! hello!
1 hello! 2 hello! 3 hello!
1 hello! 2 hello! 3 hello!
Solution
B.
Earlier we saw this example:
i = 0
while i < 3:
print(i)
i = i + 1 # increment i by 1
0
1
2
The code snippet from this question is similar to the above example except that instead of print(i), we have print('hello!'). This means that hello! gets printed 3 times.
i = 0
while i < 3:
print('hello!')
i = i + 1
hello!
hello!
hello!
Question 2
What do you think the output of the following will be?
i = 3
while i > 0:
print('{} times 5 is'.format(i))
print(i*5)
i = i - 1
print('Done!')
i times 5 is 1 i times 5 is 2 i times 5 is 3 Done!
1 times 5 is 5 2 times 5 is 10 3 times 5 is 15 Done!
3 times 5 is 15 Done! 2 times 5 is 10 Done! 1 times 5 is 5 Done!
3 times 5 is 15 2 times 5 is 10 1 times 5 is 5 Done!
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 3
Question 4
Construct a while loop that will result in the following output
30
33
36
39
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 5
Will the following two programs produce the same output?
Program 1
i = 0
while i < 5:
print(-i)
i = i + 1
Program 2
i = 0
while i > -5:
print(i)
i = i - 1
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 6
What do you think the output of the following will be?
i = 1
while i < 100:
print(i)
i = 3*i
1 3 9 27 81
3
1 3 9 12 ... 99
1 33 66 99
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 7
What do you think the output of the following will be?
count = 0
i = 0
while i < 25:
count = count + 1
i = i + 3
print(count)
Solution
Solution is locked
