3.14. For Loops With Conditionals#
Just like we saw with while loops, we can put conditionals inside our
for loops.
Here is an example with an if statement.
for i in range(5):
print(i)
if i == 3:
print("Third time's the charm!")
0
1
2
3
Third time's the charm!
4
What’s happening here?
We have used range(5), which means that i will take on the values [0,
1, 2, 3, 4]. At each iteration we execute the code block:
print(i)
if i == 3:
print("Third time's the charm!")
At the first iteration i = 0. We print(i) and output
0
Since the condition i == 3 is False, we move onto the next iteration.
At the second iteration i = 1. We print(i) and output
1
Since the condition i == 3 is False, we move onto the next iteration.
At the third iteration i = 2. We print(i) and output
2
Since the condition i == 3 is False, we move onto the next iteration.
At the fourth iteration i = 3. We print(i) and output
3
This time the condition i == 3 is True, so we also output
Third time's the charm!
At the fifth iteration i = 4. We print(i) and output
4
Since the condition i == 3 is False we don’t do anything else. Since 4
is the last number in the sequence, we exit the loop.
This is how we can represent this code diagrammatically.
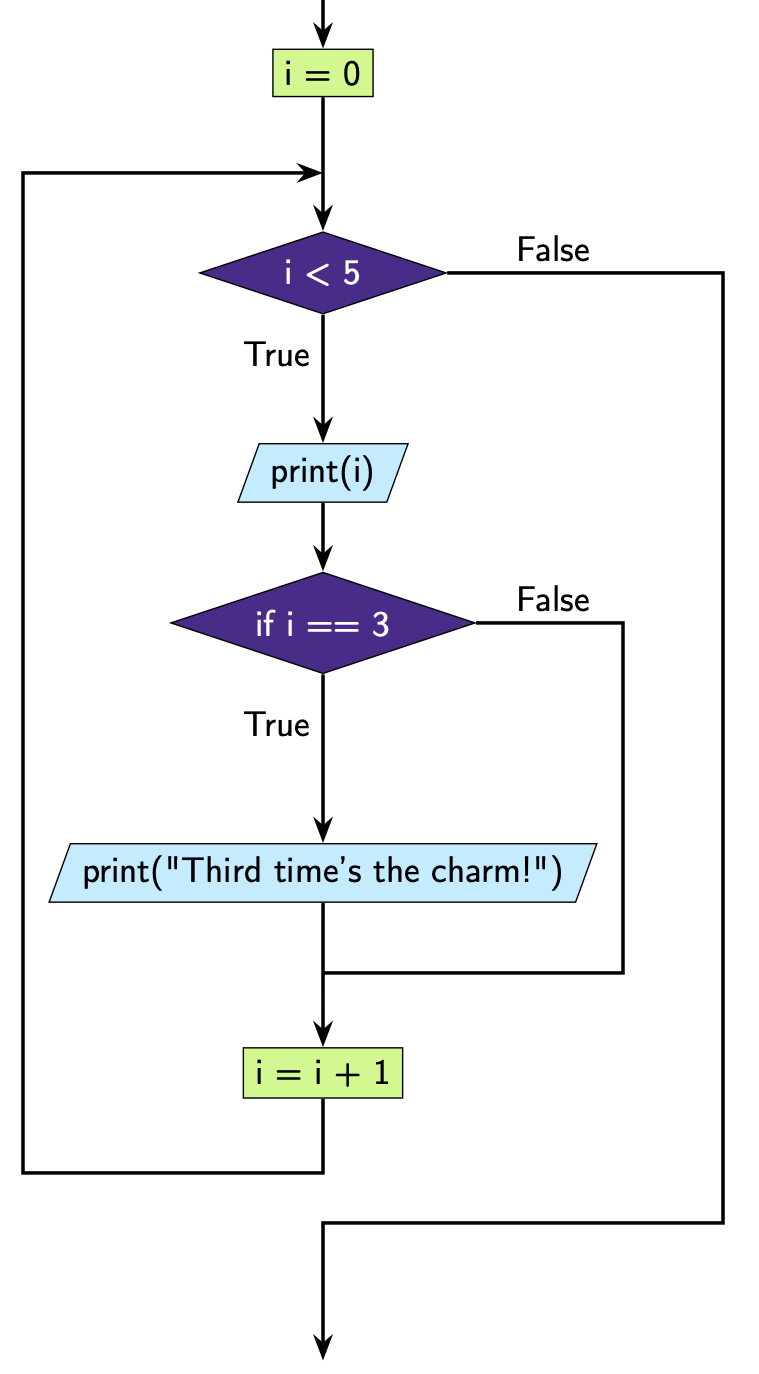
Question 1
What do you think the output of the following code will be?
for i in ['alligators', 'bears', 'cows']:
print('I like {}!'.format(i))
if i == 'alligators':
print('CRUNCH')
if i == 'bears':
print('GRRRRRRR')
if i == 'cows':
print('MOOOOOOO')
Solution
Let’s trace through this code.
We can see our iterable is the list ['alligators', 'bears', 'cows'], and i is our variable name.
At the first iteration, i will store the first value in our list i.e. i = 'alligators'. Then we will execute the code on line 2 and print
I like alligators!
Then we’ll check the if conditions, only the first condition i == 'alligators' is True, so we print
CRUNCH
At the second iteration, i will store the second value in our list i.e. i = 'bears'. Then we will execute the code on line 2 and print
I like bears!
Then we’ll check the if conditions, only the second condition i == 'bears' is True, so we print
GRRRRRRR
At the third iteration, i will store the third value in our list i.e. i = 'cows'. Then we will execute the code on line 2 and print
I like cows!
Then we’ll check the if conditions, only the third condition i == 'cows' is True, so we print
MOOOOOOO
Question 2
What do you think the output of the following code will be?
foods = ['sushi', 'burger', 'falafel', 'waffles', 'lasagne', 'sundae', 'dumplings']
for i in range(len(foods)):
if i % 2 == 0:
print(foods[i])
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
0 2 4 6
sushi falafel lasagne dumplings
burger waffles sundae
sushi burger falafel waffles lasagne sundae dumplings
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 3
What do you think the output of the following will be?
plays = ['Hamlet', 'Romeo and Juliet', 'Julius Caesar', 'Othello', 'King Lear', 'Macbeth']
long = 0
for i in plays:
if len(i) > 10:
long = long + 1
print(long)
Hint
Did you know you can use len() to check the number of characters in a string?
print(len('abc'))
3
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 4
Code challenge: Count Up and Down
Write a program that reads in an integer, and counts from 0 up to, or down to, that integer.
Example 1
Enter a number: 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
Example 2
Enter a number: -3
0
-1
-2
-3
Solution
Solution is locked
Code challenge: Crazy Case
Write a program that takes in input from the user and coverts every second letter to upper case, and every other letter to lower case. The first letter should be upper case.
Example
hello there
HeLlO ThErE
Hint
You can treat strings as lists of characters, e.g.:
sample_string = 'Hello!'
print(sample_string[5])
!
You can also convert characters to upper and lower case using .upper() and .lower()
print('a'.upper())
print('A'.lower())
A
a
Solution
Solution is locked
Code challenge: Prime Number
Write a program that asks the user for a number. If the given number is a prime number the program should print
n is a prime number
otherwise your program should print
n is not a prime number
Example 1
n: 347
347 is a prime number
Example 2
n: 102
102 is not a prime number
Solution
Solution is locked
