3.16. Nested Loops#
You can make the block of code inside the loops as complex as you want. This
means you can also put loops inside other loops, whether they be while
loops or for loops.
Example: multiplication tables with nested for loops.
for i in range(1, 13):
for j in range(1, 13):
print("{} x {} = {}".format(i, j, i * j))
1 x 1 = 1
1 x 2 = 2
1 x 3 = 3
...
12 x 11 = 132
12 x 12 = 144
What’s happening here?
We can see that at the first iteration of the outer loop, i = 1. Then
we run the code block inside this for loop, which is
for j in range(1, 13):
print("{} x {} = {}".format(i, j, i * j))
This is another for loop, this time with j looping from 1, …, 12, each
time printing '{} x {} = {}'.format(i, j, i*j). Note that for the entire
duration of this loop running i is still 1. This means we get 1 x 1 =
1, …, 1 x 12 = 12.
We can see that at the second iteration of the outer loop, i = 2. Again
we run the code block inside this for loop, which is
for j in range(1, 13):
print("{} x {} = {}".format(i, j, i * j))
This loop will again run in its entirety with j looping from 1, …, 12,
each time printing '{} x {} = {}'.format(i, j, i*j). For the entire
duration of this loop running i is still 2. This means we get 2 x 1 =
2, …, 2 x 12 = 24.
We keep running through the outer loop for i = 1, …, 12, each time
running the inner loop. This gives us all of the standard multiplication
tables.
Note that the iteration variables you use in your outer and inner loops need
to have different variable names, otherwise you will overwrite the value of
the iteration variable used in your outer loop. In this example our outer
iteration variable is i and our inner iteration variable is j.
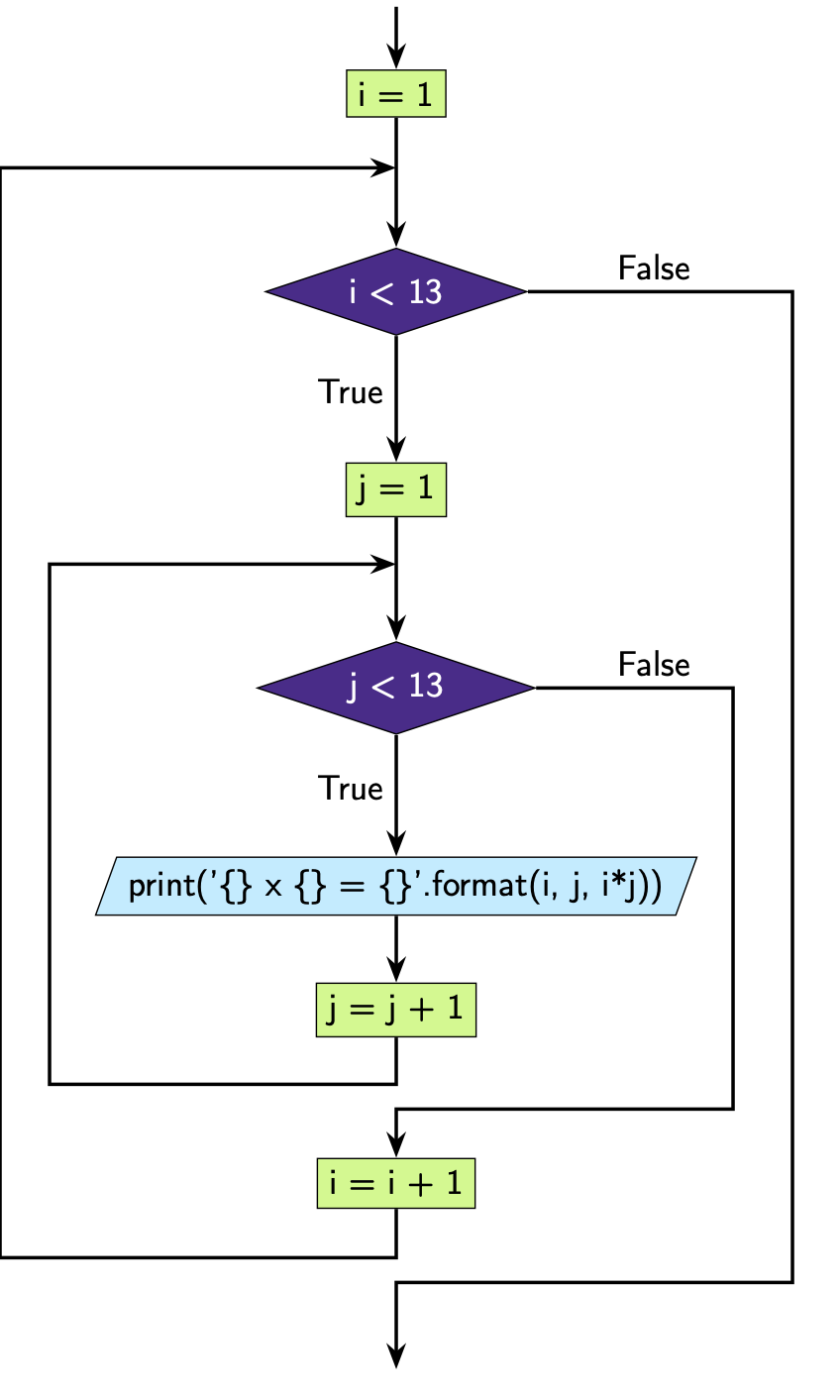
Example: multiplication tables with nested while loops.
i = 1
while i < 13:
j = 1
while j < 13:
print("{} x {} = {}".format(i, j, i * j))
j = j + 1
i = i + 1
Example: multiplication tables with a while loop inside a for loop.
for i in range(1, 13):
j = 1
while j < 13:
print("{} x {} = {}".format(i, j, i * j))
j = j + 1
Question 1
Write a program with an outer while loop and an inner for loop that prints out the standard multiplication table from \(1\times1\) to \(12\times 12\), as shown below.
1 x 1 = 1
1 x 2 = 2
1 x 3 = 3
...
12 x 11 = 132
12 x 12 = 144
Solution
i = 1
while i < 13:
for j in range(1, 13):
print('{} x {} = {}'.format(i, j, i * j))
i = i + 1
Question 2
What do you think the output of the following code will be?
n = 5
for i in range(n):
line = ''
for j in range(n):
line = line + '*'
print(line)
* ** *** **** *****
***** ***** ***** *****
* * * * *
* * * * *
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 3
Write a program that will prints out all of the date for every day of the year. You have been provided with the months and days list which tells you the number of days in each month (for a non-leap year).
months = ['Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar', 'Apr', 'May', 'Jun', 'Jul', 'Aug', 'Sept', 'Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec']
days = [31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31]
The output of your program should look like this.
Jan 1
Jan 2
...
Dec 30
Dec 31
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 4
Code challenge: Alarm Clock
Write a program that simulates an alarm clock set for 7:00 am. The program should count each minute from 0:00 through to 7:00, after which time it will tell the user to WAKE UP!!!.
Your program should look like this:
0:00
0:01
0:02
0:03
0:04
0:05
...
6:55
6:56
6:57
6:58
6:59
WAKE UP!!!
Solution
Solution is locked
Code challenge: Grid
Write a program that asks the user for an integer \(n\) and then prints out an \(n\) grid.
Example 1
n: 1
+ - +
| |
+ - +
Example 2
n: 5
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
Solution
Solution is locked
Code challenge: X Marks The Spot
Write a program that asks the user for an integer \(n\), and co-ordinates \(x\) and \(y\). Your program should then print out an \(n\times n\) grid and places an x at the co-ordinates \((x, y)\). In this co-ordinate system the top left corner is \((1, 1)\), as shown in the diagram below.
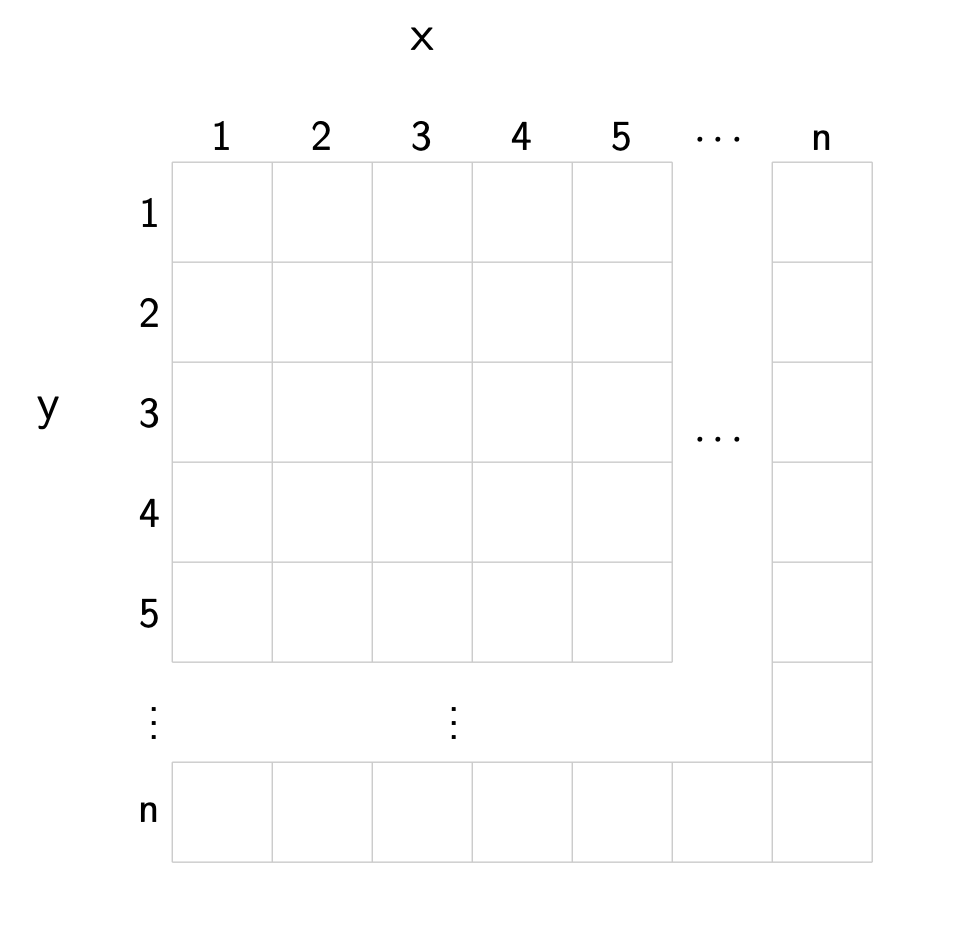
Example 1
n: 5
x: 2
y: 3
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | x | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - +
Example 2
n: 8
x: 6
y: 2
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | | x | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - +
| | | | | | | | |
+ - + - + - + - + - + - + - + - +
