3.10. While Loops With Input#
It is often useful to use a while loop to request information from a user
until they enter a specific string that will cause the loop to terminate.
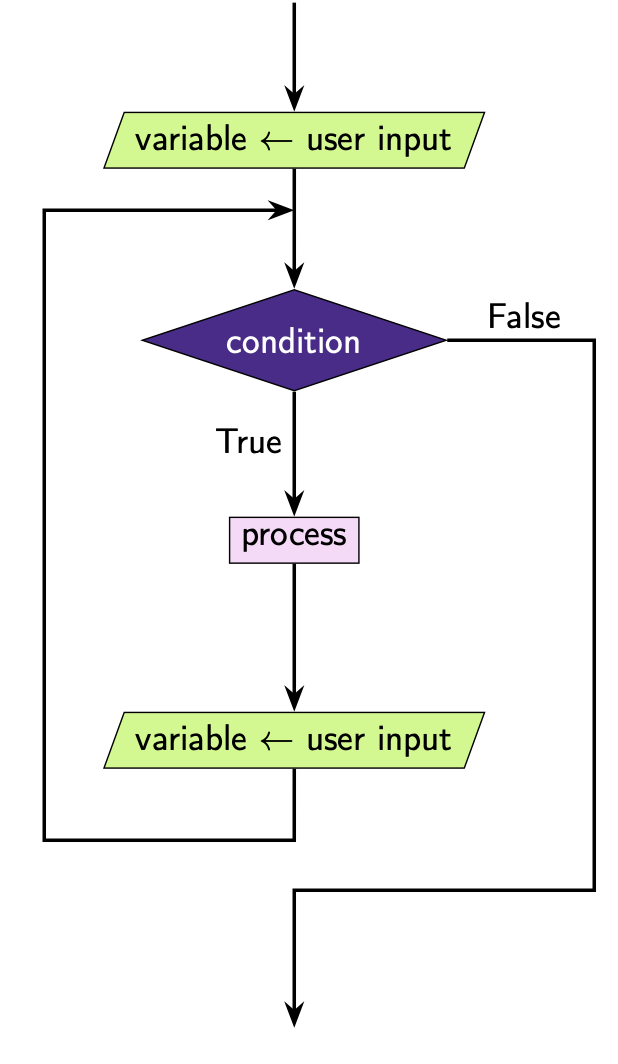
It’s important to note that this time the variable we check in our loop is
obtained via input(). This means we represent it with a parallelogram
in our flowchart.
Here is an example.
number = input("Enter a number: ")
while number != "5":
print(number)
number = input("Enter a number: ")
What you’ll notice is that each time you enter a number, the program will
repeat that number unless that number is 5. If the user enters a 5, the
condition number != 5 is False and the loop terminates.
This is how we can represent this code diagrammatically.
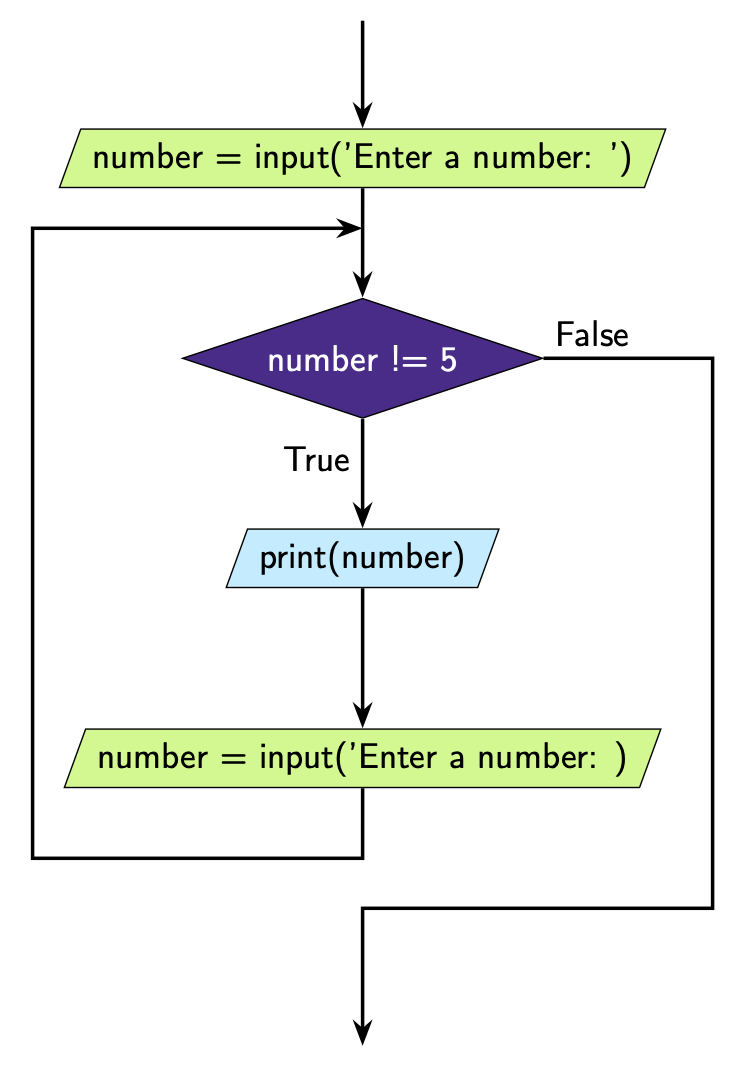
Note that it looks a little different to our previous diagrams. The main difference are:
We aren’t iterating through a series of sequential values. The user decides what the next value of number will be.
The condition we are checking is that
numberis not a specific value (in this casenumberis not 5).numberis not actually a number at all it’s a string!
A very common string to terminate on is the empty string '', i.e. the
program will terminate if the user presses enter without giving any other
input.
number = input("Enter a number: ")
while number != "":
print(number)
number = input("Enter a number: ")
Question 1
What’s wrong with the following code snippet?
colour = input('Enter a colour: ')
while colour != 'blue':
print(colour)
print("That's my favourite colour!")
This will result in a NameError because colour is not defined.
This will result in a SyntaxError because
!=is not a valid comparison operatorThis will result in a ValueError as the
!=operator only works for integersThe code will result in an infinite loop if the user enters a colour that is not blue because colour is never updated.
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 2
Construct a while loop the asks the user to Enter a word and terminates if the user enters the word stop. When the program terminates it should say Program has stopped.
An example of how this program might run is shown below with user input shown in bold.
Enter a word: full
Enter a word: non
Enter a word: door
Enter a word: stop
Program has stopped
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 3
Suppose you ran the following code.
print('Guess a number between 1 and 10')
guesses = 1
n = input()
while n != '2':
guesses = guesses + 1
n = input()
print('Correct! That took you {} guess(es)!'.format(guesses))
The user guesses the values 4, 9 and then 2. What would the output of this program look like (including the lines containing user input).
Solution
Solution is locked
Code challenge: Echo Forever
Write a program that echoes back everything the user says, but stops as soon as the user stops saying things (i.e. they press enter).
Example 1
Hello
Hello
How are you?
How are you?
Example 2
The weather is nice today.
The weather is nice today.
Don't you think?
Don't you think?
Yes I do.
Yes I do.
Hint
You can check whether a user hasn’t provided any input by comparing the input to an empty string ''. The condition you will want to use is: != ''
Solution
Solution is locked
Code challenge: Add To The List
Write a program that asks the user what they need to buy. The program should continuously read in each item the user needs to buy and add it to a Python list, stopping as soon as the user enters a blank line. The program should print out the resultant list.
Example 1
What do you need to buy?
apples
oranges
['apples', 'oranges']
Example 2
What do you need to buy?
pears
pineapples
peaches
papayas
passionfruits
['pears', 'pineapples', 'peaches', 'paypayas', 'passionfruits']
Solution
Solution is locked
Code challenge: What Is The Password?
Write a program that asks the user to enter a password. If the password is in the list of passwords, the program should say Welcome back!. If the password is not in the list, it should say Not a valid password. While the password is invalid, the program should keep asking the user to enter a password.
The examples given use the following password list:
passwords = ['open sesame', 'password', '12345']
Example
Enter password: apple
Not a valid password.
Enter password: orange
Not a valid password.
Enter password: pear
Not a valid password.
Enter password: 12345
Welcome back!
Hint
Python has the keywords in and not in which can be used to check if a word is in a list or not.
animals = ['python', 'quokka', 'zebra']
print('quokka' in animals)
print('snake' not in animals)
True
True
Solution
Solution is locked